

Data
Benchmarks
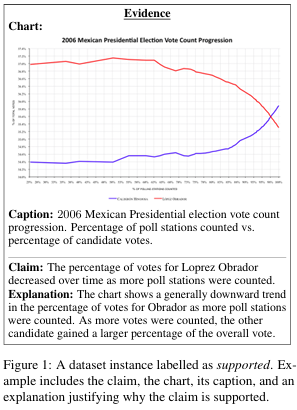
ChartCheck: An Evidence-Based Fact-Checking Dataset over Real-World Chart Images
Whilst fact verification has attracted substan tial interest in the natural language processing community, verifying misinforming statements against data visualizations such as charts has so far been overlooked. Charts are commonly used in the real-world to summarize and com municate key information, but they can also be easily misused to spread misinformation and promote certain agendas. In this paper, we introduce ChartCheck, a novel, large-scale dataset for explainable fact-checking against Chart: Evidence real-world charts, consisting of 1.7k charts and 10.5k human-written claims and explanations. We systematically...
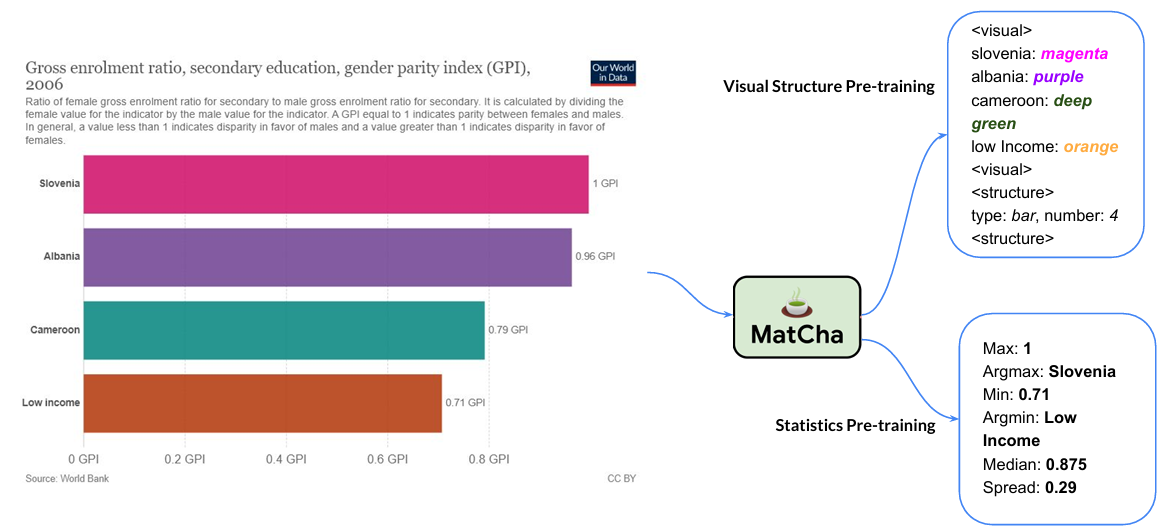
Enhancing Question Answering on Charts Through Effective Pre-training Tasks
To completely understand a document, the use of textual information is not enough. Under standing visual cues, such as layouts and charts, is also required. While the current state-of the-art approaches for document understanding (both OCR-based and OCR-free) work well, we have not found any other works conduct ing a thorough analysis of their capabilities and limitations. Therefore, in this work, we ad dress the limitation of current VisualQA mod els when applied to charts and plots. To in vestigate shortcomings of the state-of-the-art models, we conduct a comprehensive behav ioral analysis, using ChartQA as a case study. Our findings ...
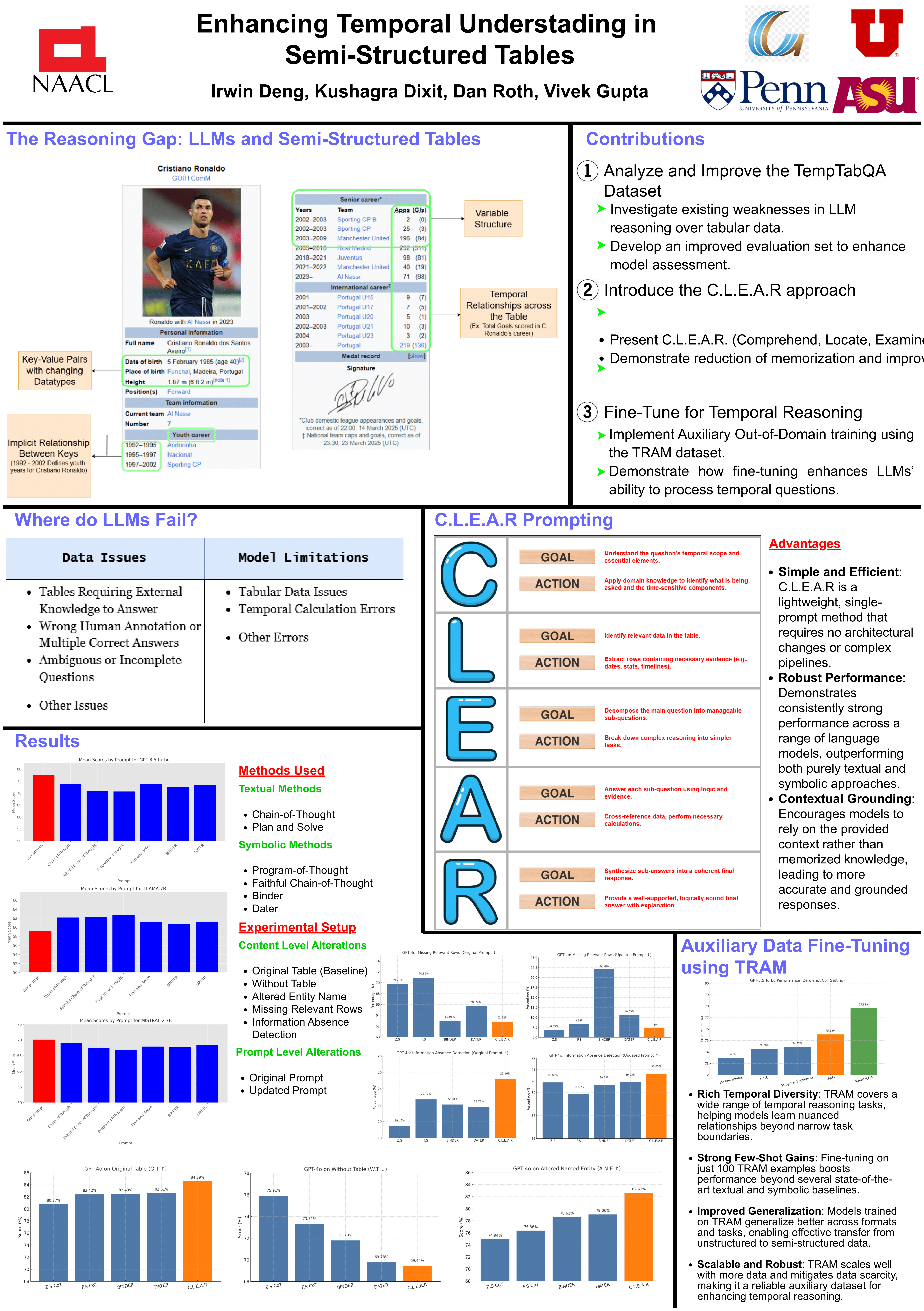
Enhancing Temporal Understanding in LLMs for Semi-structured Tables
Temporal reasoning over tabular data presents substantial challenges for large language mod els (LLMs), as evidenced by recent research. In this study, we conduct a comprehensive analy sis of temporal datasets to pinpoint the specific limitations of LLMs. Our investigation leads to enhancements in TempTabQA, a benchmark specifically designed for tabular temporal ques tion answering. We provide critical insights for enhancing LLM performance in temporal reasoning tasks with tabular data. Furthermore, we introduce a novel approach, C.L.E.A.R to strengthen LLM capabilities in this domain. Our findings demonstrate that our method im proves evidence-based reasoning across various models. Additionally, our experimental...
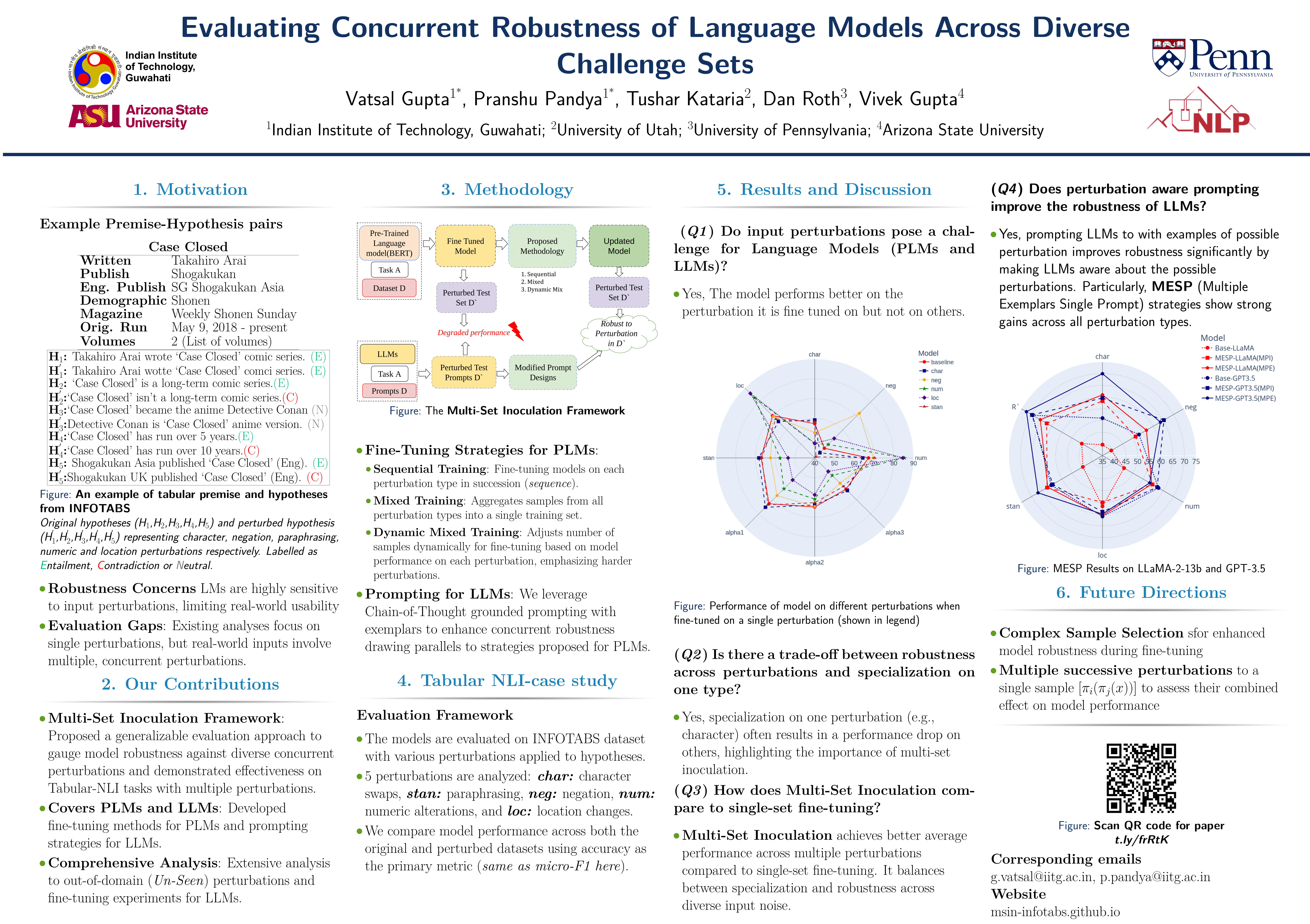
Evaluating Concurrent Robustness of Language Models Across Diverse Challenge Sets
Language models, characterized by their black box nature, often hallucinate and display sensitivity to input perturbations, causing concerns about trust. To enhance trust, it is imperative to gain a comprehensive understanding of the model’s failure modes and develop effective strategies to improve their performance. In this study, we introduce a methodology designed to examine how input perturbations affect language models across various scales, including pre-trained models and large language models (LLMs). Utilizing fine-tuning, we enhance the model’s robustness to input perturbations. Additionally, ...

Evaluating LLMs' Mathematical Reasoning in Financial Document Question Answering
Large Language Models excel at language understanding but their mathematical reasoning over complex financial tables and text is uncertain; this study benchmarks them on TATQA, FinQA, ConvFinQA, and Multihiertt to assess sensitivity to table complexity and arithmetic reasoning steps.

Federated Retrieval-Augmented Generation: A Systematic Mapping Study
Federated Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Federated RAG) combines federated learning with retrieval-augmented generation to ground outputs in external knowledge while keeping data private; this mapping study surveys Federated RAG work from 2020–2025 in privacy-sensitive domains.
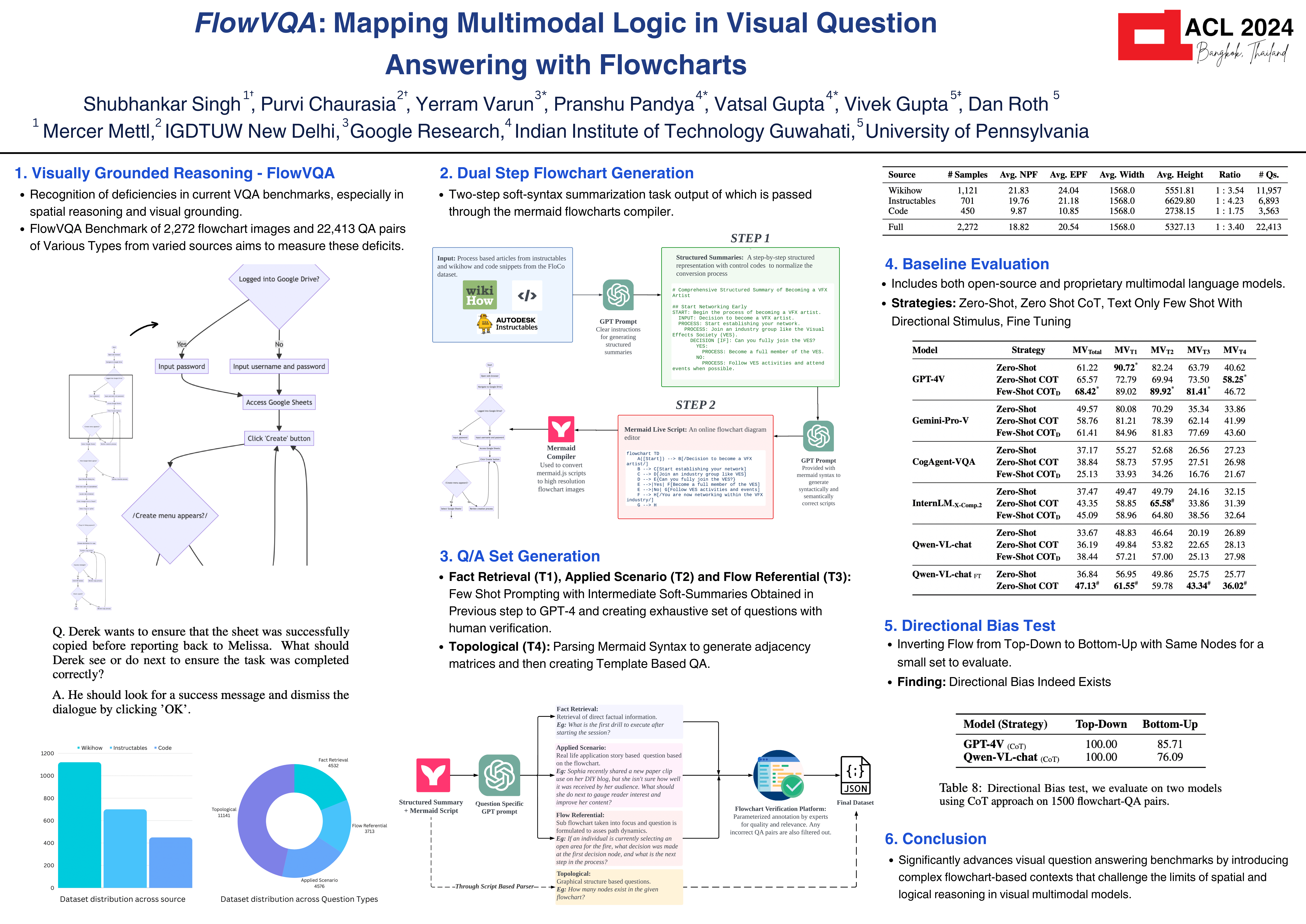
FlowVQA: Mapping Multimodal Logic in Visual Question Answering with Flowcharts
Visual QA benchmark over 2,272 flowcharts and 22,413 Q&A pairs spanning factual, referential, and topological reasoning.

Follow the Flow: Fine-grained Flowchart Attribution with Neurosymbolic Agents
Fine-grained Flowchart Attribution traces flowchart components grounding LLM responses to reduce hallucinated connections; FlowPathAgent is a neurosymbolic agent that segments flowcharts and applies graph-based reasoning for verifiable, explainable answers.
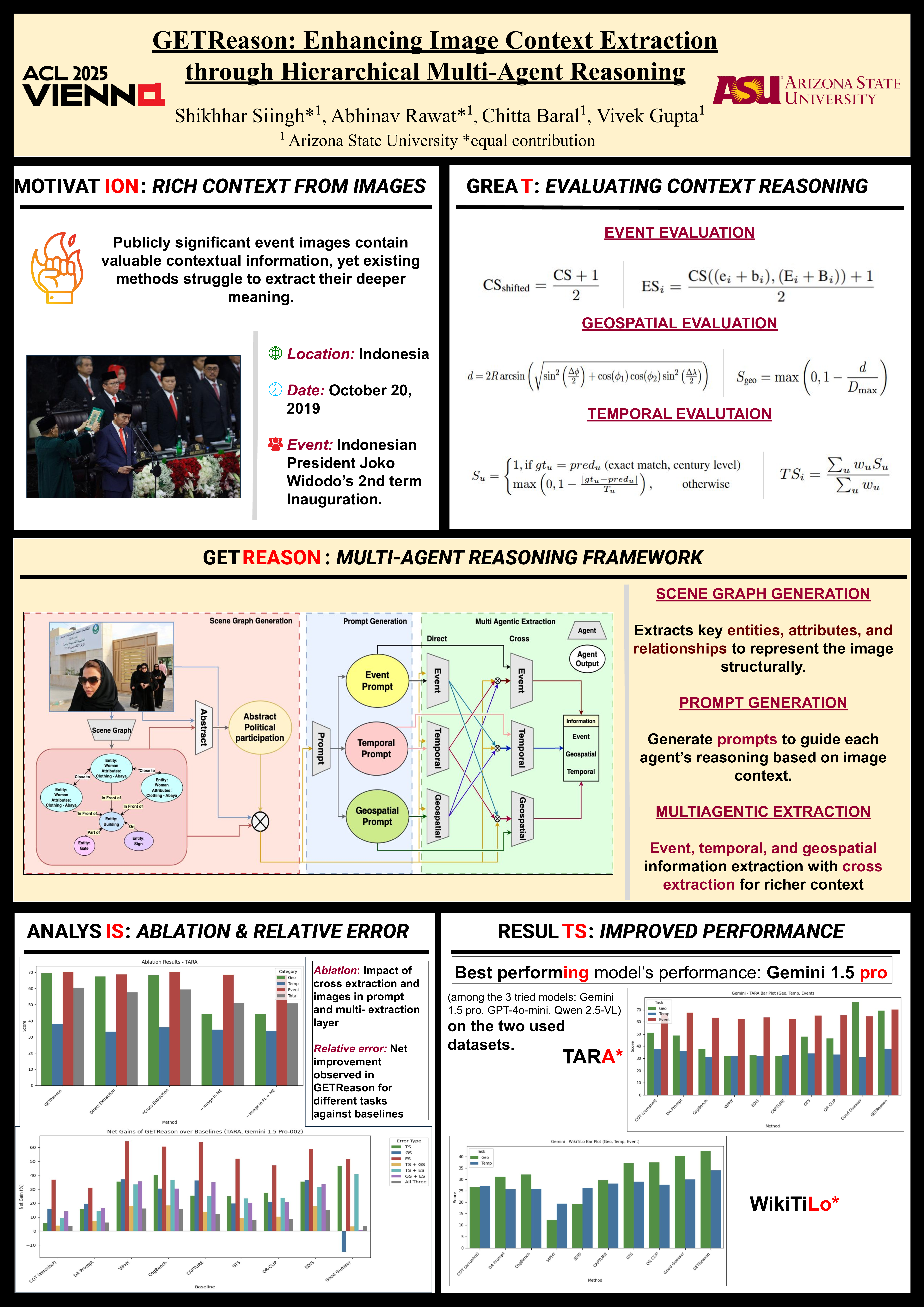
GETReason: Enhancing Image Context Extraction through Hierarchical Multi-Agent Reasoning
Publicly significant images from events carry valuable contextual information with applications in domains such as journalism and education. However, existing methodologies of ten struggle to accurately extract this contextual relevance from images. To address this challenge, we introduce GETREASON(Geospatial Event Temporal Reasoning), a framework designed to go beyond surface level image descriptions and infer deeper con textual meaning. We hypothesize that ex tracting global event, temporal, and geospa tial information from an image enables a more accurate understanding of its contex tual significance. We also introduce a new metric GREAT (Geospatial, Reasoning and Event Accuracy with Temporal alignment) for a reasoning capturing evaluation. Our lay ered multi-agentic approach, evaluated...

H-STAR: LLM-driven Hybrid SQL-Text Adaptive Reasoning on Tables
Tabular reasoning involves interpreting natural language queries about tabular data, which presents a unique challenge of combining language understanding with structured data analysis. Existing methods employ either textual reasoning, which excels in semantic interpretation but struggles with mathematical operations, or symbolic reasoning, which handles computations well but lacks semantic understanding. This paper introduces a novel algorithm H-STAR that integrates both symbolic and semantic (textual) approaches in a two-stage process to address these limitations. H-STAR employs: (1) step-wise table extraction using ‘multi-view’ column retrieval followed by row extraction, and (2) adaptive reasoning that adapts reasoning strategies based on question types, utilizing semantic reasoning for direct lookup and complex lexical queries while augmenting textual reasoning with symbolic reasoning support for quantitative and logical tasks. Our extensive...

InfoSync: Synchronizing Information Across Tables
Multilingual table synchronization dataset spanning ~99k infoboxes across 14 languages for alignment and update tasks.

InfoTab: A Benchmark for Table-based Information Extraction
Dataset of 23,738 entailment pairs grounded in Wikipedia infoboxes for table-based NLI.
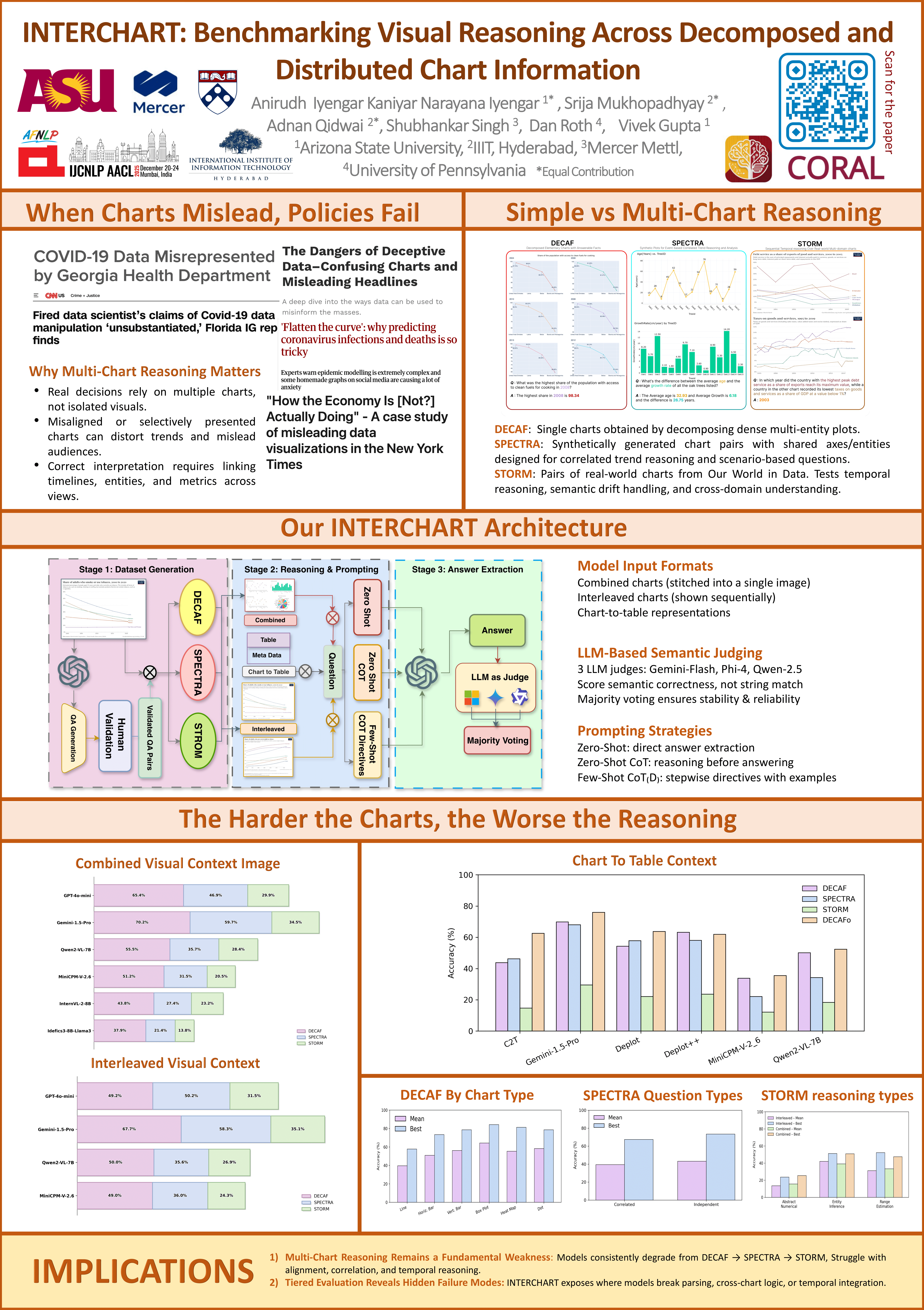
InterChart: Benchmarking Visual Reasoning Across Decomposed and Distributed Chart Information
InterChart is a diagnostic benchmark for VLM reasoning across related charts with questions spanning entity inference, trend correlation, numerical estimation, and multi-step reasoning over 2–3 thematically linked charts across three difficulty tiers.
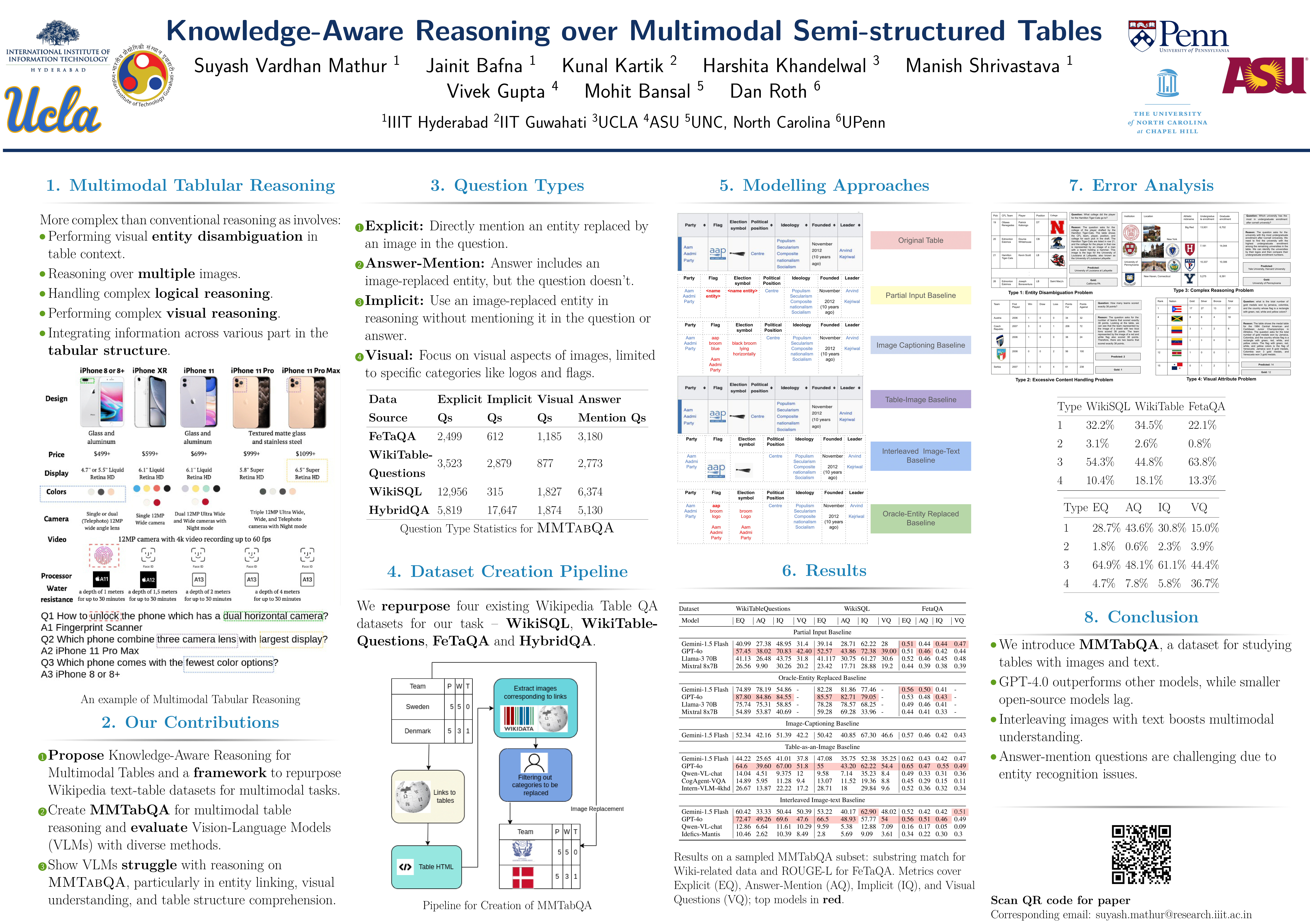
Knowledge-Aware Reasoning over Multimodal Semi-structured Tables
Existing datasets for tabular question answer ing typically focus exclusively on text within cells. However, real-world data is inherently multimodal, often blending images such as symbols, faces, icons, patterns, and charts with textual content in tables. With the evo lution of AI models capable of multimodal reasoning, it is pertinent to assess their effi cacy in handling such structured data. This study investigates whether current AI models can perform knowledge-aware reasoning on multimodal structured data. We explore their ability to reason on tables that integrate both images and text, introducing MMTABQA, a new dataset designed for this purpose. Our experiments...
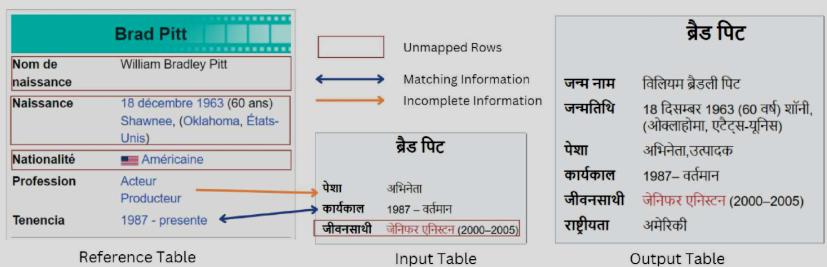
Leveraging LLM for Synchronizing Information Across Multilingual Tables
The vast amount of online information today poses challenges for non-English speakers, as much of it is concentrated in high-resource languages such as English and French. Wikipedia reflects this imbalance, with content in low-resource languages frequently outdated or incomplete. Recent research has sought to improve cross-language synchronization of Wikipedia tables using rule-based methods. These approaches can be effective, but they struggle with complexity and generalization. This paper explores large language models (LLMs) for multilingual information synchronization, using zero-shot prompting as a scalable solution. We introduce the Information Updation dataset, simulating the real-world process of updating outdated Wikipedia tables, and evaluate LLM performance. Our findings...
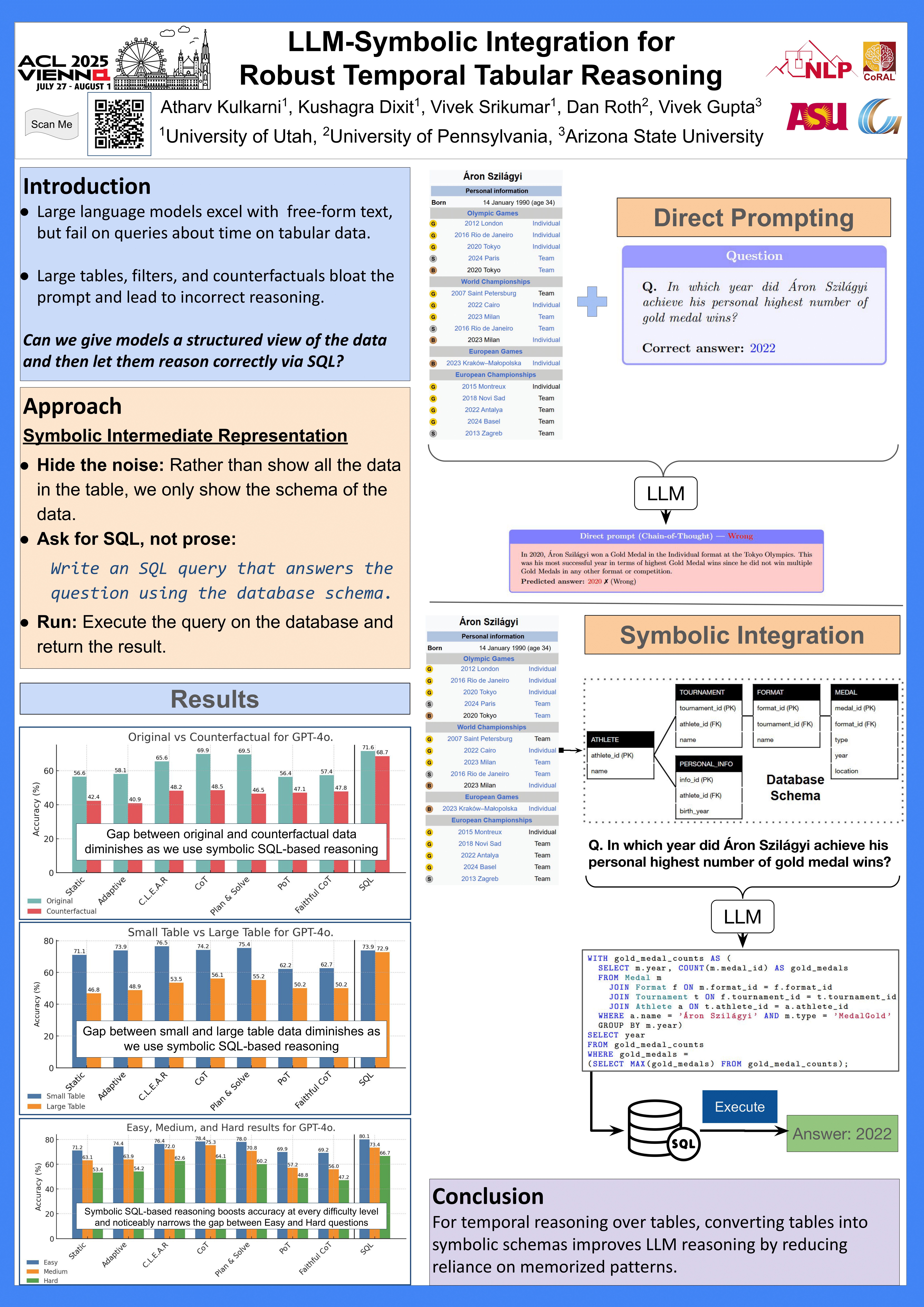
LLM-Symbolic Integration for Robust Temporal Tabular Reasoning
Temporal tabular question answering presents a significant challenge for Large Language Models (LLMs), requiring robust reasoning over structured data—a task where traditional prompting methods often fall short. These methods face challenges such as memorization, sensitivity to table size, and reduced performance on complex queries. To overcome these limitations, we introduce TEMPTABQA-C, a synthetic dataset designed for systematic and controlled evaluations, alongside a symbolic intermediate representation that transforms tables into database schemas. This structured approach allows LLMs to generate and execute SQL queries, enhancing generalization and mitigating biases. By incorporating...

M-HELP: Using Social Media Data to Detect Mental Health Help-Seeking Signals
Mental health disorders are a global crisis; M-HELP is a dataset to detect help-seeking behavior on social media, labeling specific disorders and causes like relationship or financial stressors, to train AI models for support.
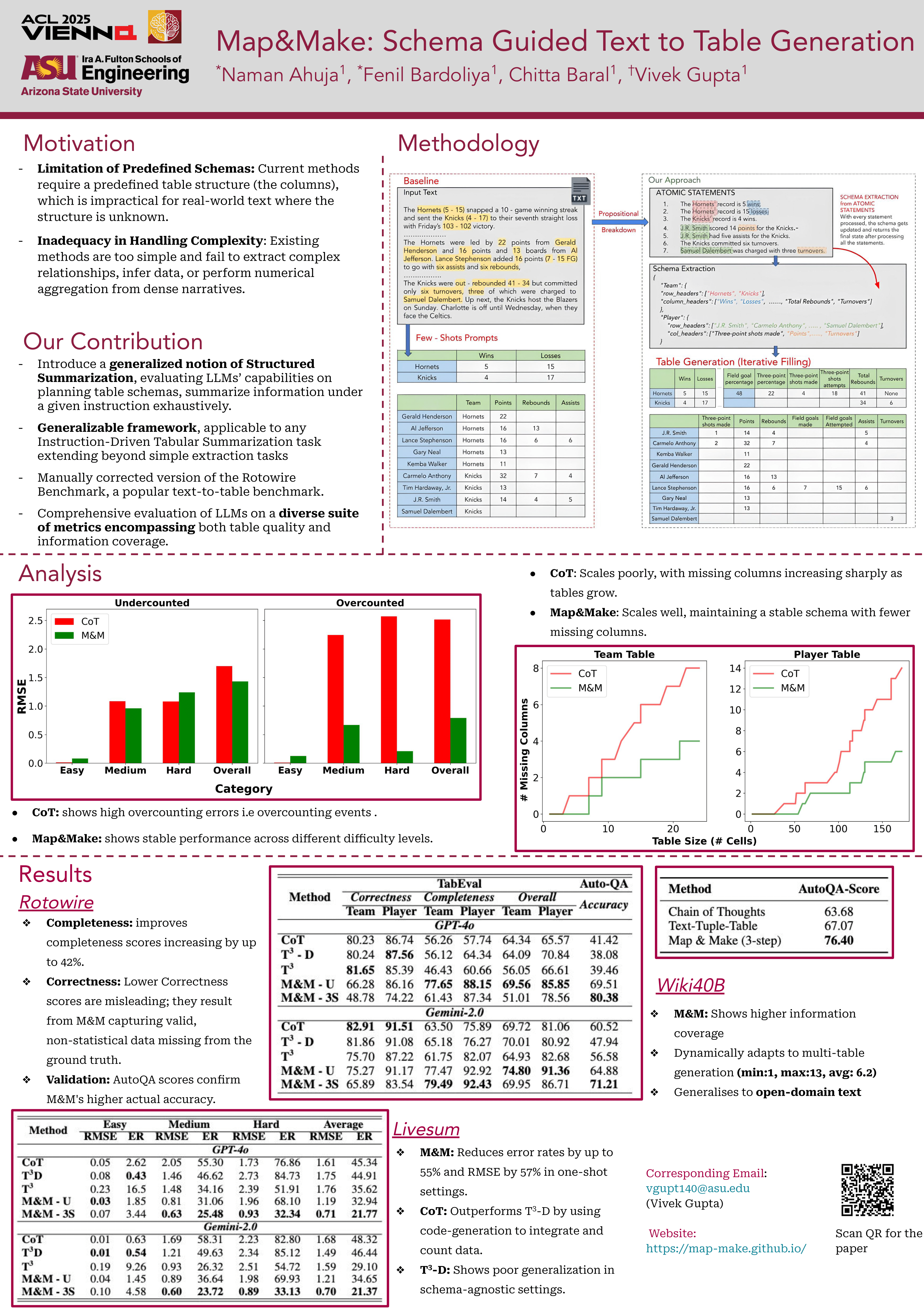
Map&Make: Schema Guided Text to Table Generation
Transforming dense, unstructured text into interpretable tables—commonly referred to as Text-to-Table generation—is a key task in information extraction. Existing methods often overlook what complex information to extract and how to infer it from text. We present Map&Make, a versatile approach that decomposes text into atomic propositions to infer latent schemas, which are then used to generate tables capturing both qualitative nuances and quantitative facts. We evaluate...
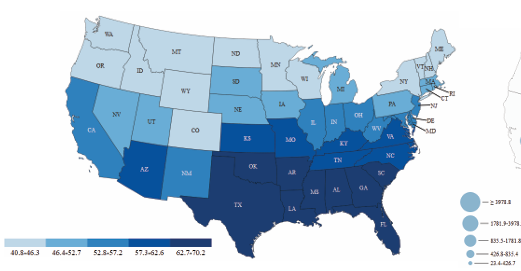
MapIQ: Benchmarking Multimodal Large Language Models for Map Question Answering
Recent advancements in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have driven researchers to explore how well these models read data visualizations, e.g., bar charts, scatter plots. More recently, attention has shifted to visual question answering with maps (Map-VQA). However, Map-VQA research has primarily focused on choropleth maps, which cover only a limited range of thematic categories and visual analytical tasks. To address these gaps, we introduce MapIQ, a benchmark dataset comprising 14,706 question-answer pairs across three map types—choropleth maps, cartograms, and proportional symbol maps spanning topics from six distinct themes (e.g., housing, crime). We evaluate multiple MLLMs using six visual analytical tasks, comparing their performance against one another and a human baseline. An additional experiment...
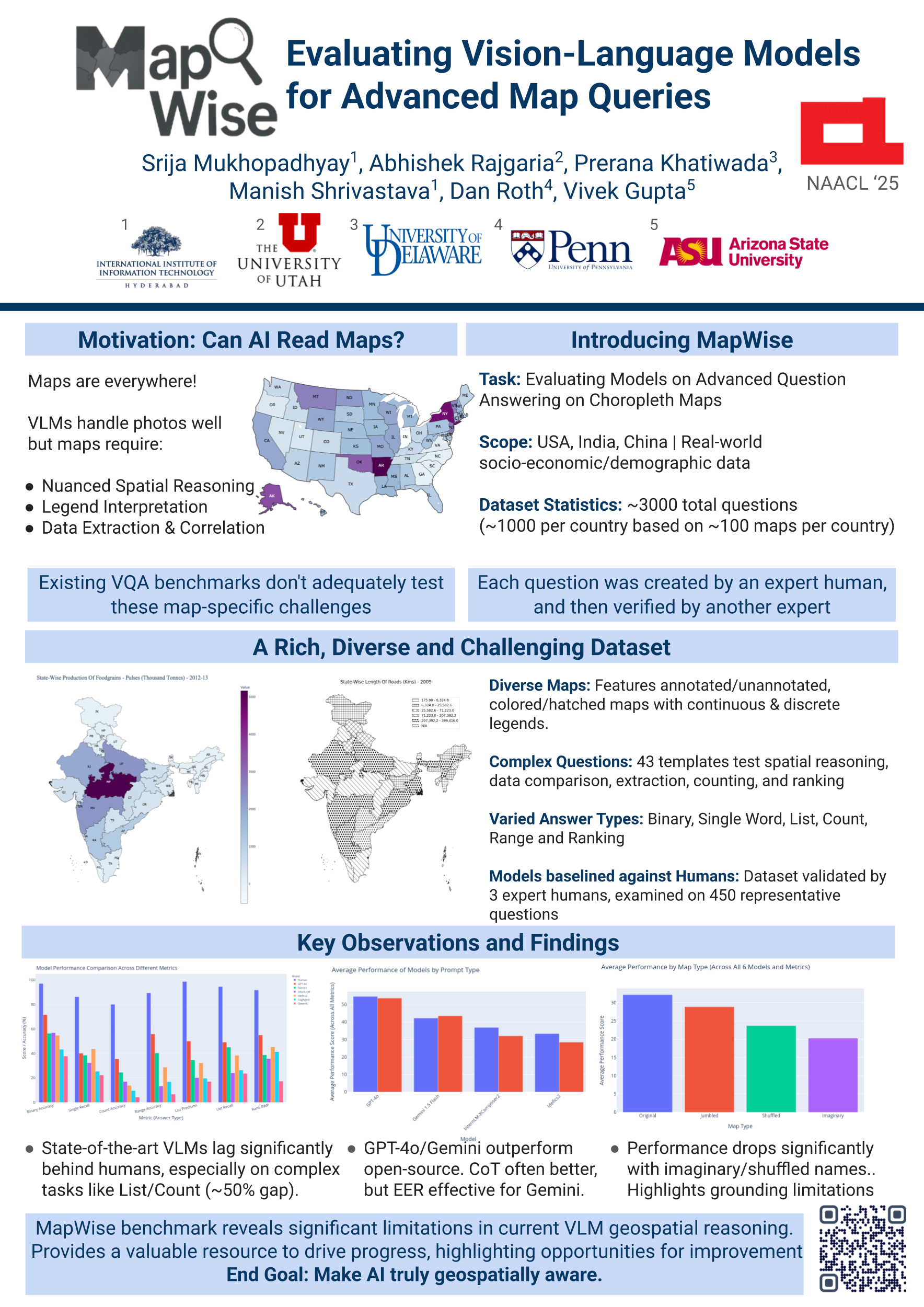
MAPWise: Evaluating Vision-Language Models for Advanced Map Queries
Vision-language models (VLMs) excel at tasks requiring joint understanding of visual and lin guistic information. A particularly promising yet under-explored application for these models lies in answering questions based on various kinds of maps. This study investigates the efficacy of VLMs in answering questions based on choropleth maps, which are widely used for data analysis and representation. To facilitate and encourage research in this area, we intro duce a novel map-based question-answering benchmark, consisting of maps from three geographical regions (United States, India, China), each containing 1000 questions. Our benchmark...
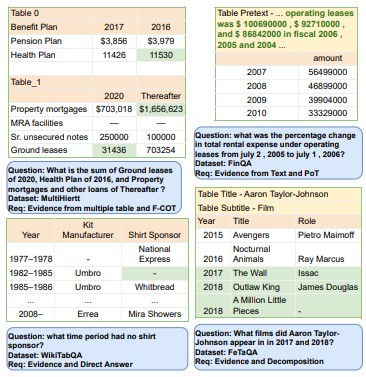
No Universal Prompt: Unifying Reasoning through Adaptive Prompting for Temporal Table Reasoning
Temporal table reasoning is challenging for LLMs across varied table structures and contexts; this work evaluates prompting techniques, shows no single method dominates, and introduces SEAR/SEAR_Unified to adapt prompts and integrate structured reasoning, improving performance with optional table refactoring.
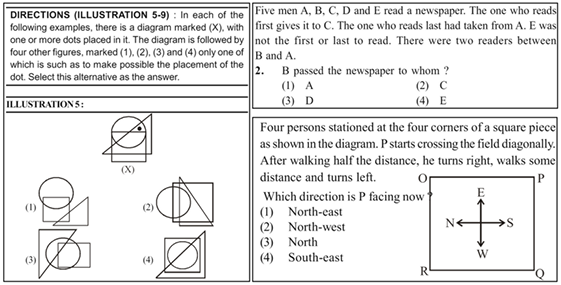
NTSEBENCH: Cognitive Reasoning Benchmark for Vision Language Models
Cognitive textual and visual reasoning tasks, including puzzles, series, and analogies, demand the ability to quickly reason, decipher, and evaluate patterns both textually and spatially. Due to extensive training on vast amounts of human-curated data, large language models (LLMs) and vision language models (VLMs) excel in common-sense reasoning tasks, but still struggle with more complex reasoning that demands deeper cognitive understanding. We introduce NTSEBENCH, a new dataset designed to evaluate cognitive multimodal reasoning and problem-solving skills of large models. The dataset contains 2,728 multiple-choice questions, accompanied by a total of 4,642 images, spanning 26 categories....
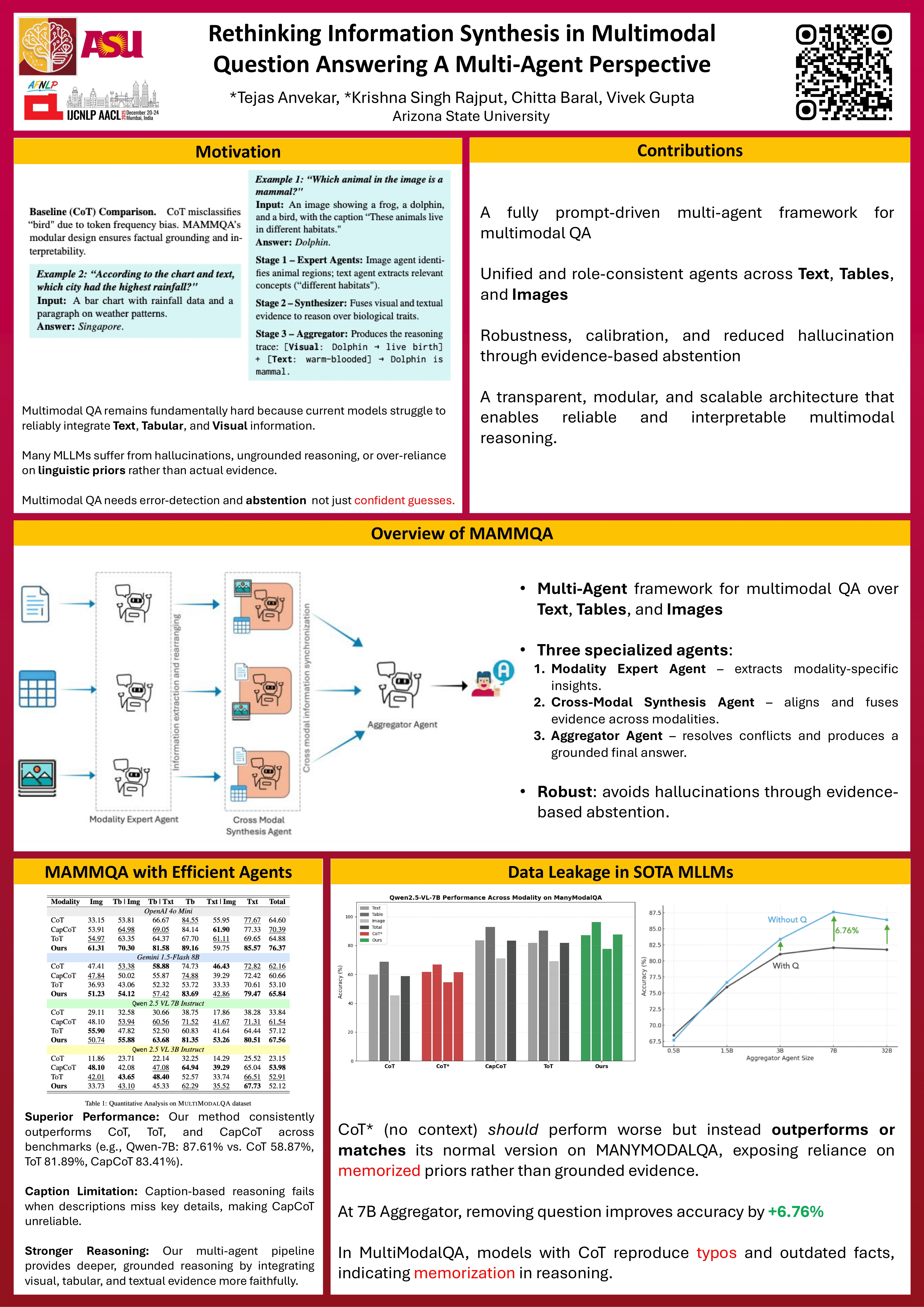
Rethinking Information Synthesis in Multimodal Question Answering A Multi-Agent Perspective
MAMMQA is a multi-agent QA framework for multimodal inputs (text, tables, images), assigning specialized reasoning per modality to improve accuracy and interpretability over single-strategy approaches.
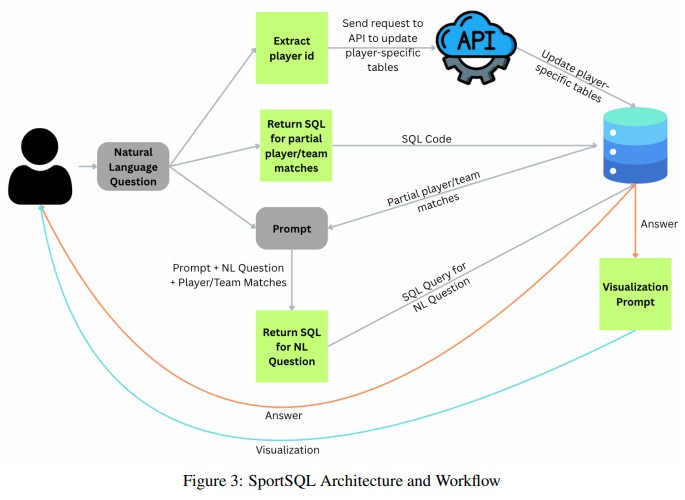
SPORTSQL: An Interactive System for Real-Time Sports Reasoning and Visualization
SPORTSQL is a modular interactive system for natural language querying and visualization of dynamic sports data; it translates questions into SQL over live Fantasy Premier League data and uses LLM-based symbolic reasoning for query parsing, schema linking, and visualization selection.
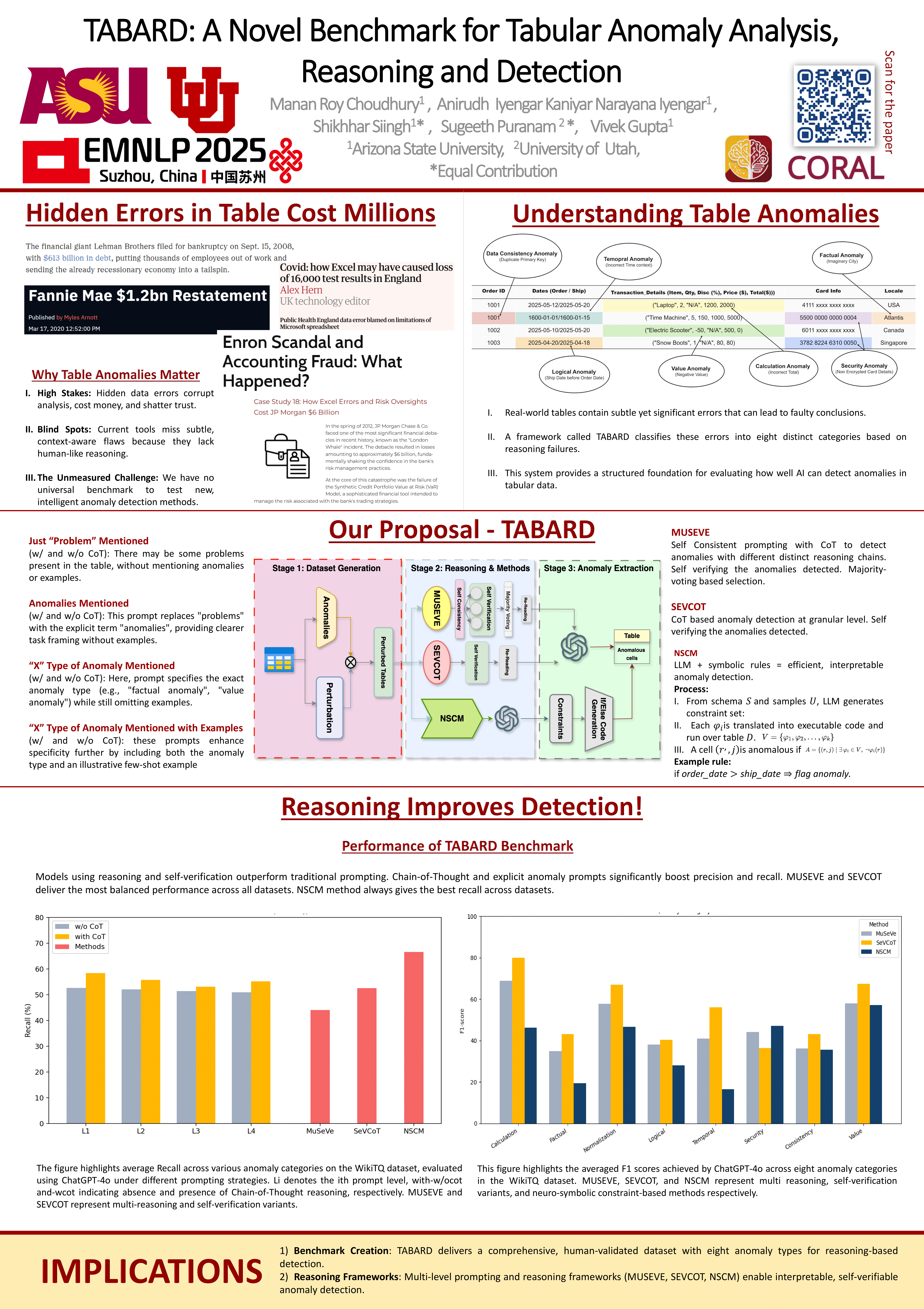
TABARD: A Novel Benchmark for Tabular Anomaly Analysis, Reasoning and Detection
TABARD is a benchmark for detecting diverse table anomalies (factual, logical, temporal, value-based) built by perturbing WikiTQ, FeTaQA, Spider, and BEAVER; it evaluates LLMs with direct, indirect, and CoT prompting and proposes a unified multi-step prompting and self-verification framework to improve accuracy.
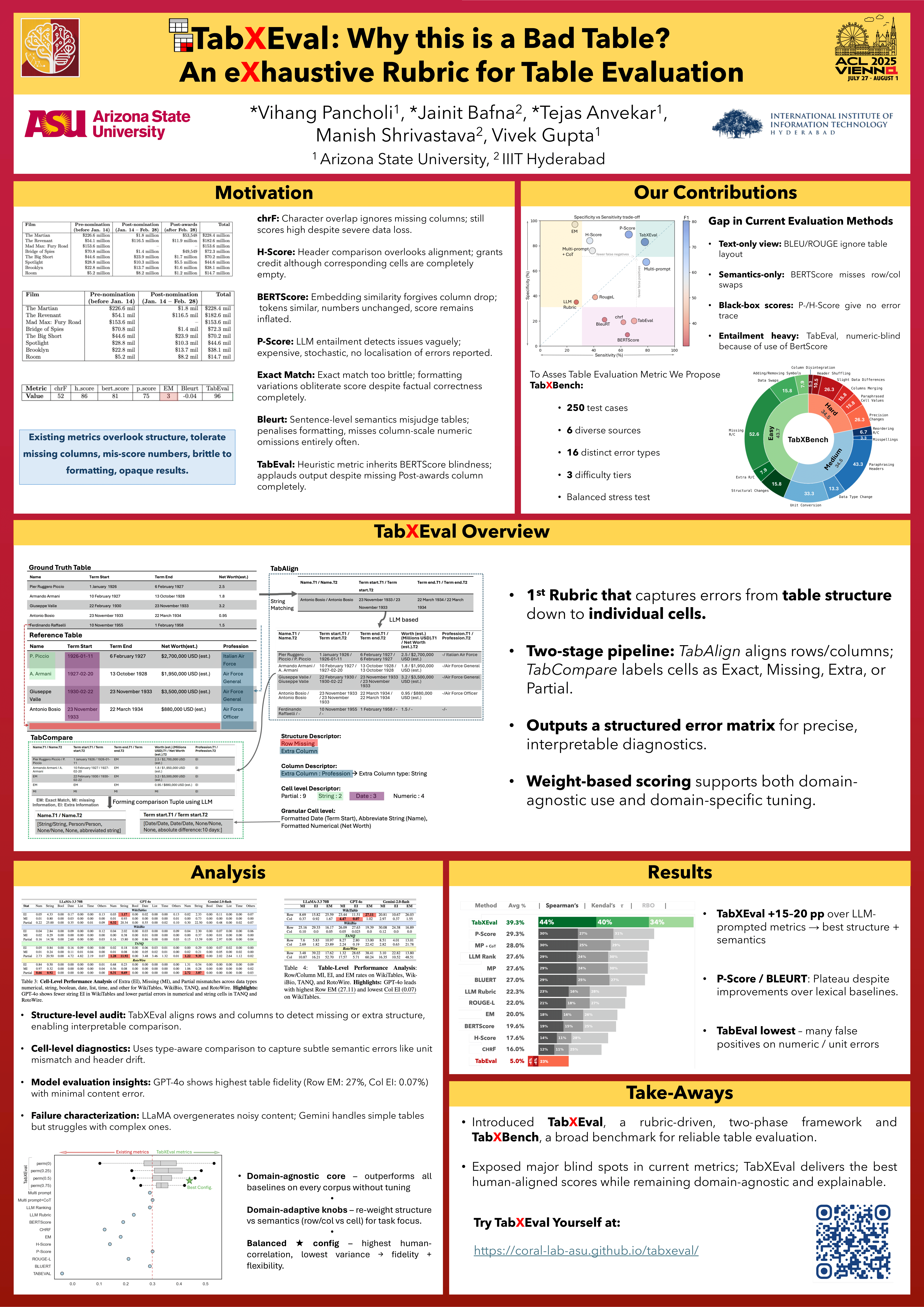
TabXEval: Why this is a Bad Table? An eXhaustive Rubric for Table Evaluation
Evaluating tables qualitatively and quantita tively poses a significant challenge, as standard metrics often overlook subtle structural and content-level discrepancies. To address this, we propose a rubric-based evaluation frame work that integrates multi-level structural de scriptors with fine-grained contextual signals, enabling more precise and consistent table comparison. Building on this, we introduce TabXEval, an eXhaustive and eXplainable two-phase evaluation framework. TabXEval first aligns reference and predicted...

TempTabQA-C
Controlled benchmark of 200,000 temporal table QA pairs with counterfactuals and varied difficulty.
TempTabQA: Temporal Table Question Answering
Dataset of 11,454 temporal QA pairs over 1,208 Wikipedia infobox tables to evaluate time-aware reasoning.
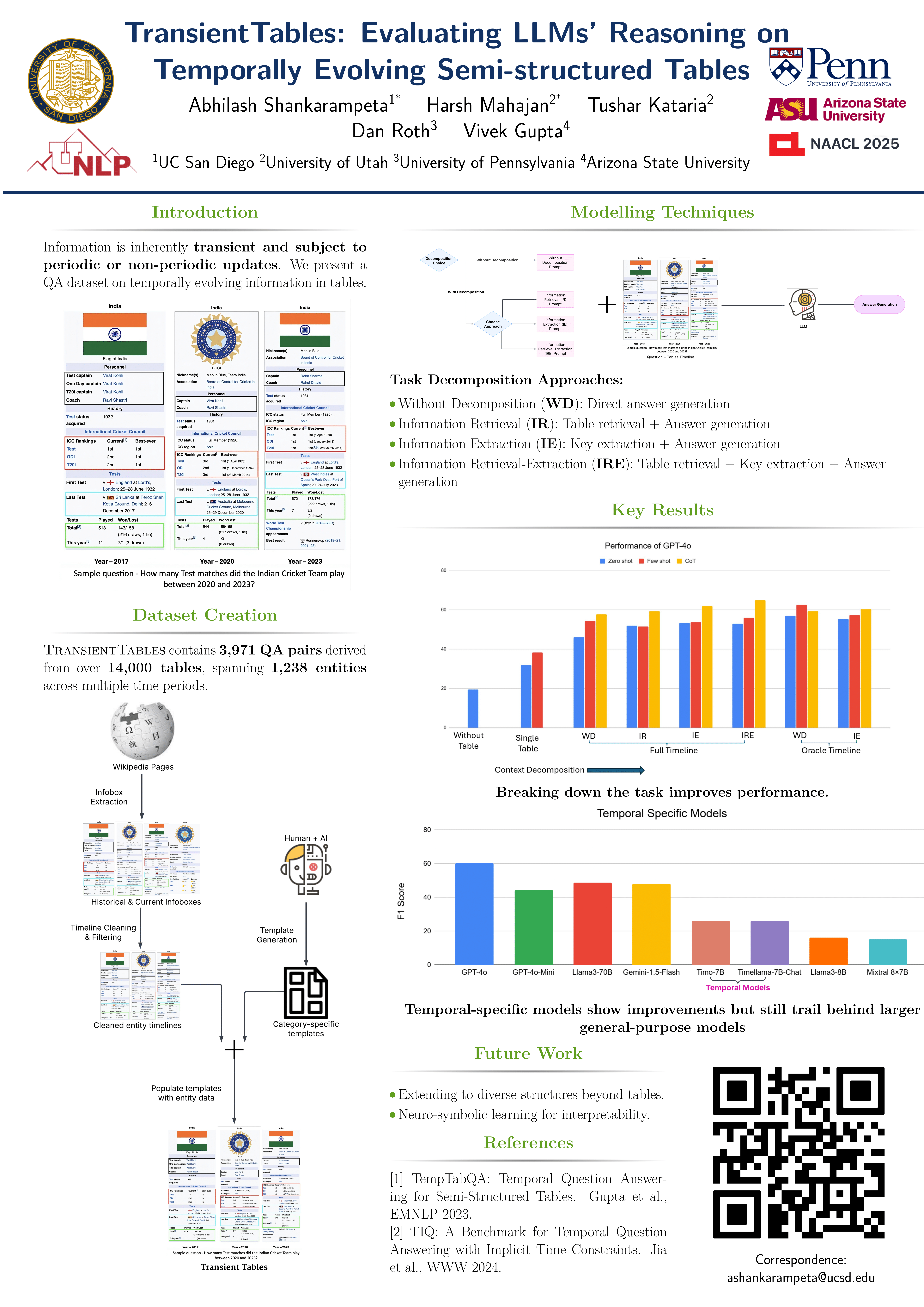
TRANSIENT TABLES: Evaluating LLMs' Reasoning on Temporally Evolving Semi-structured Tables
Presents TRANSIENTTABLES with 3,971 questions over 14k temporally evolving tables to evaluate LLM temporal reasoning, plus baselines and a template-driven generation pipeline.
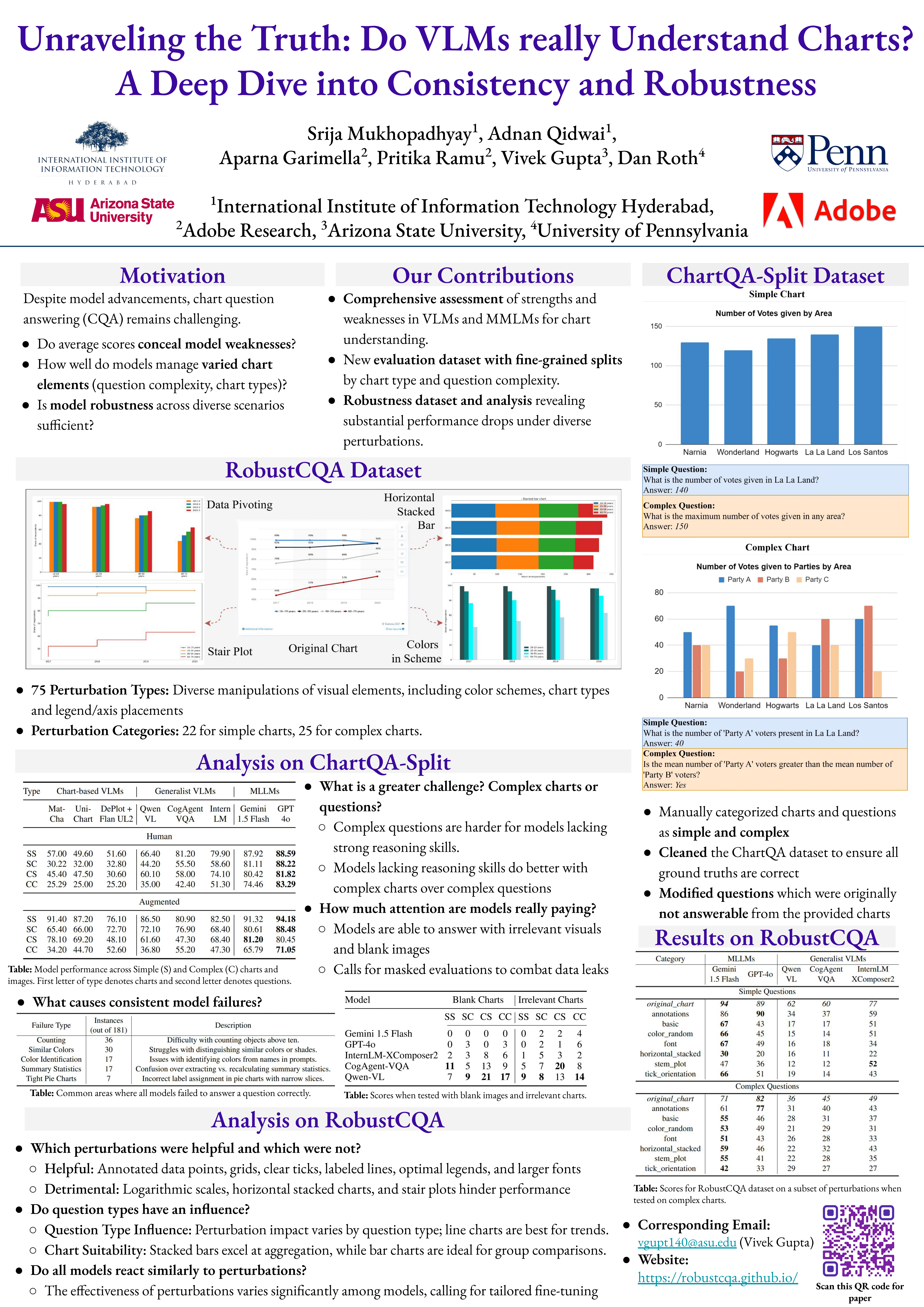
Unraveling the Truth: Do VLMs really Understand Charts? A Deep Dive into Consistency and Robustness
Chart question answering (CQA) is a crucial area of Visual Language Understanding. However, the robustness and consistency of current Visual Language Models (VLMs) in this field remain under-explored. This paper evaluates state-of-the-art VLMs on comprehensive datasets, developed specifically for this study, encompassing diverse question categories and chart formats. We investigate two key aspects: 1) the models' ability to handle varying levels of chart and question complexity, and 2) their robustness across different visual representations of the same underlying data. Our analysis reveals significant performance variations based on question and chart types, highlighting both strengths and weaknesses of current models. Additionally,...
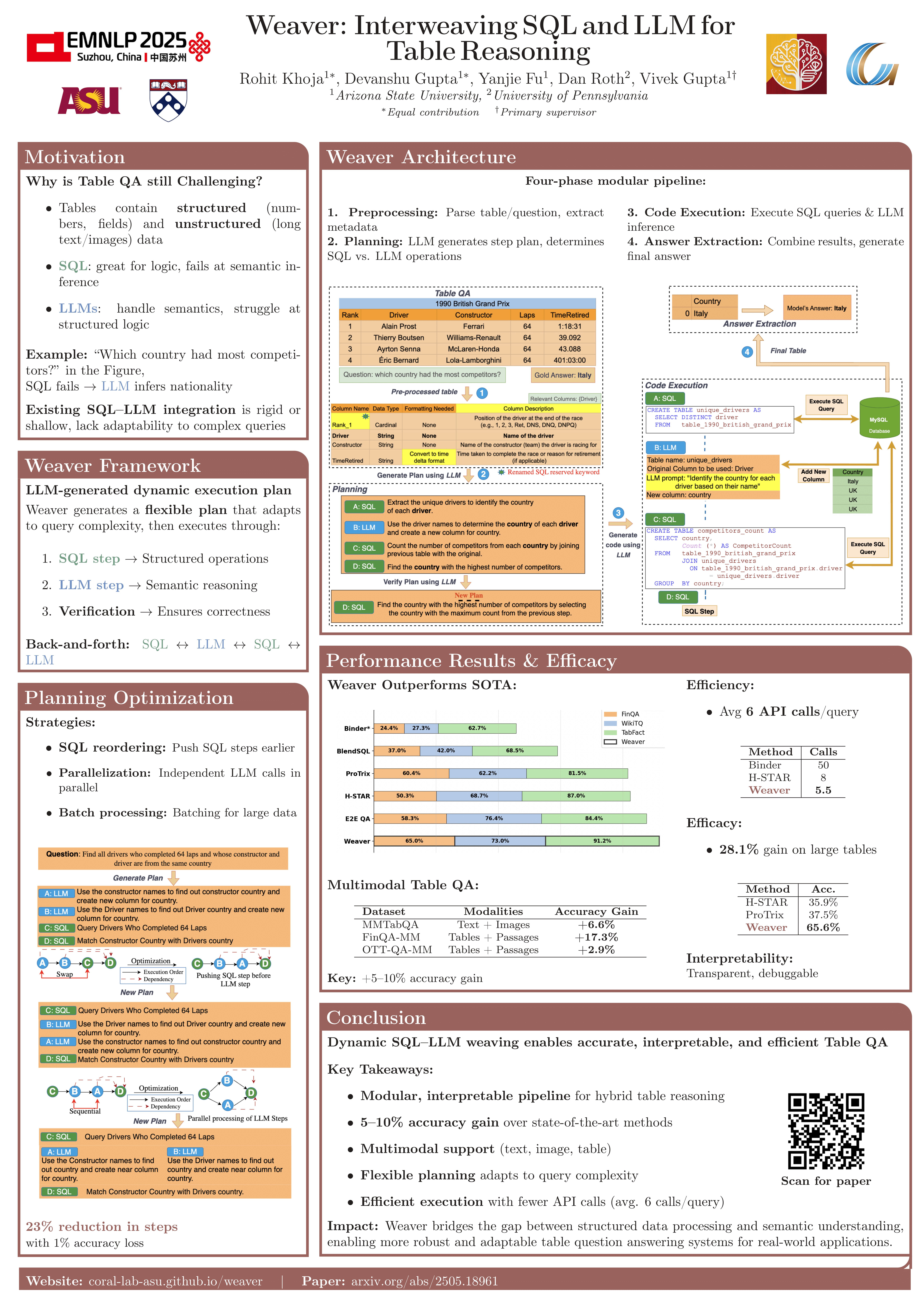
Weaver: Interweaving SQL and LLM for Table Reasoning
Weaver is a modular pipeline that dynamically weaves SQL and LLMs for table QA, handling unstructured text or images alongside tables without rigid workflows and mitigating LLM context length limits.
Demo
Software
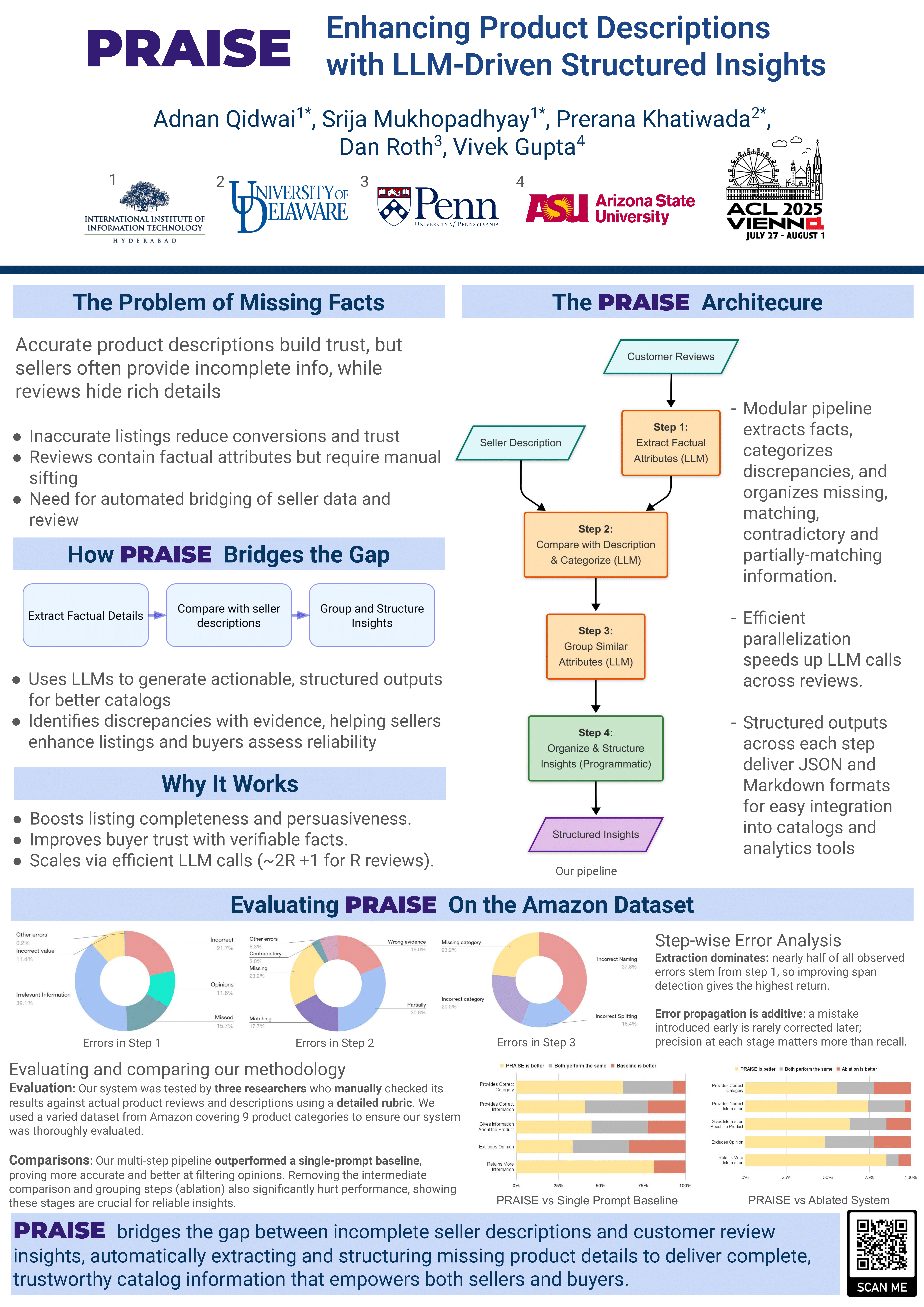
PRAISE: Enhancing Product Descriptions with LLM-Driven Structured Insights
Accurate and complete product descriptions are crucial for e-commerce, yet seller-provided information often falls short. Customer reviews offer valuable details but are laborious to sift through manually. We present PRAISE: Product Review Attribute Insight Structuring Engine, a novel system that uses Large Language Models (LLMs) to automatically extract, compare, and structure insights from customer reviews and seller descriptions. PRAISE provides users with an intuitive interface to identify missing, contradictory, or partially matching details between these two sources, presenting the discrepancies in a clear, structured format alongside supporting evidence from reviews. This allows...