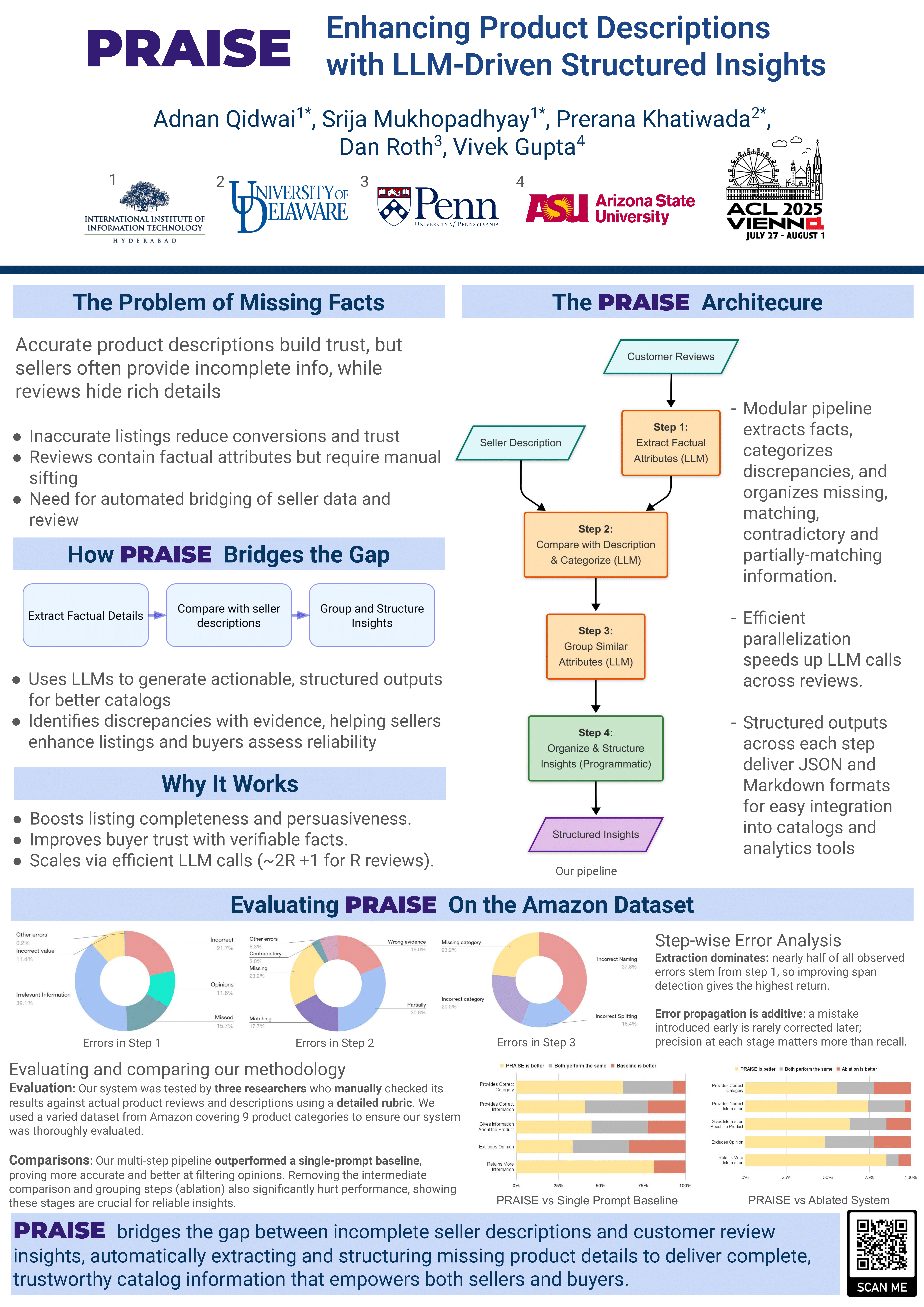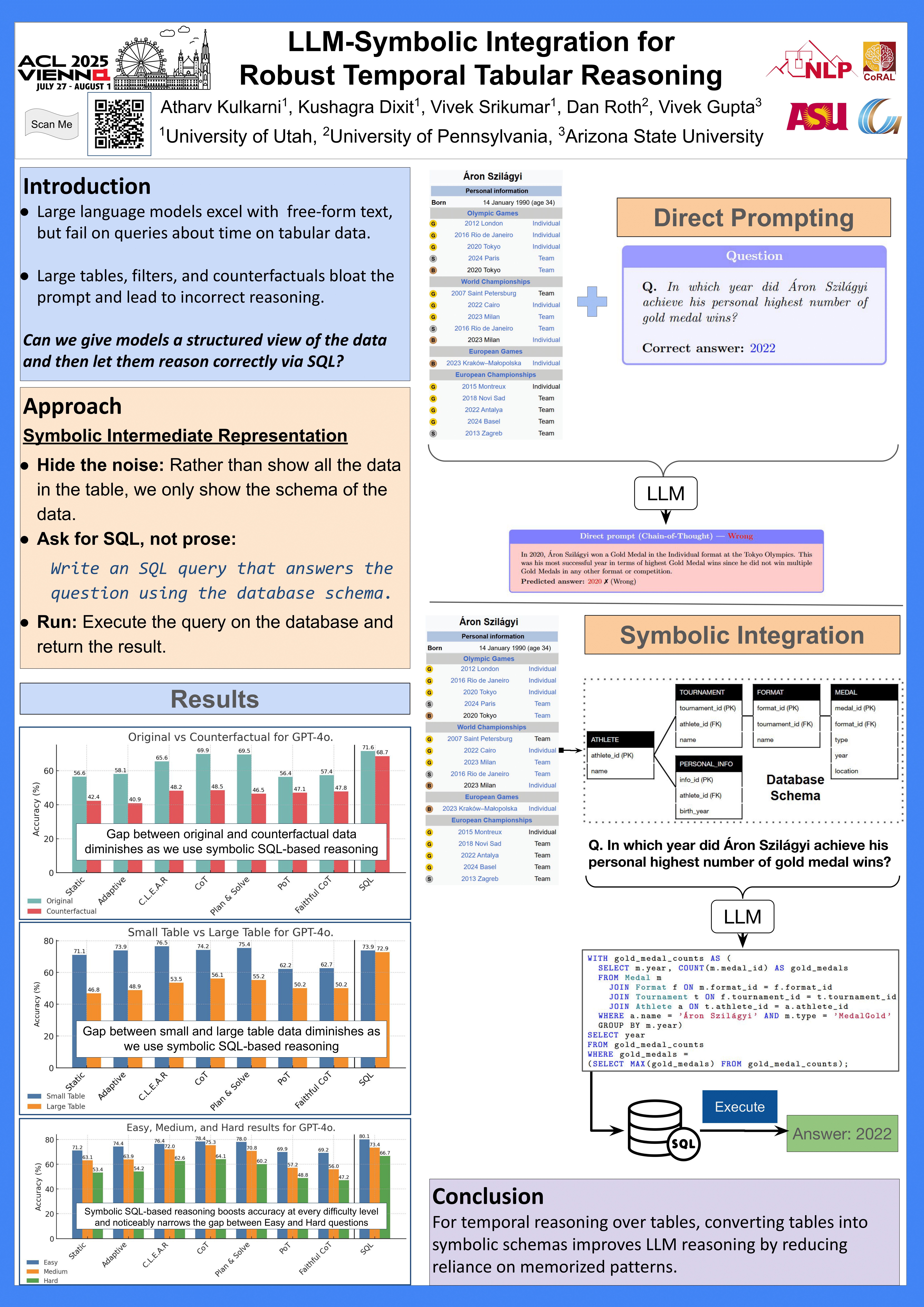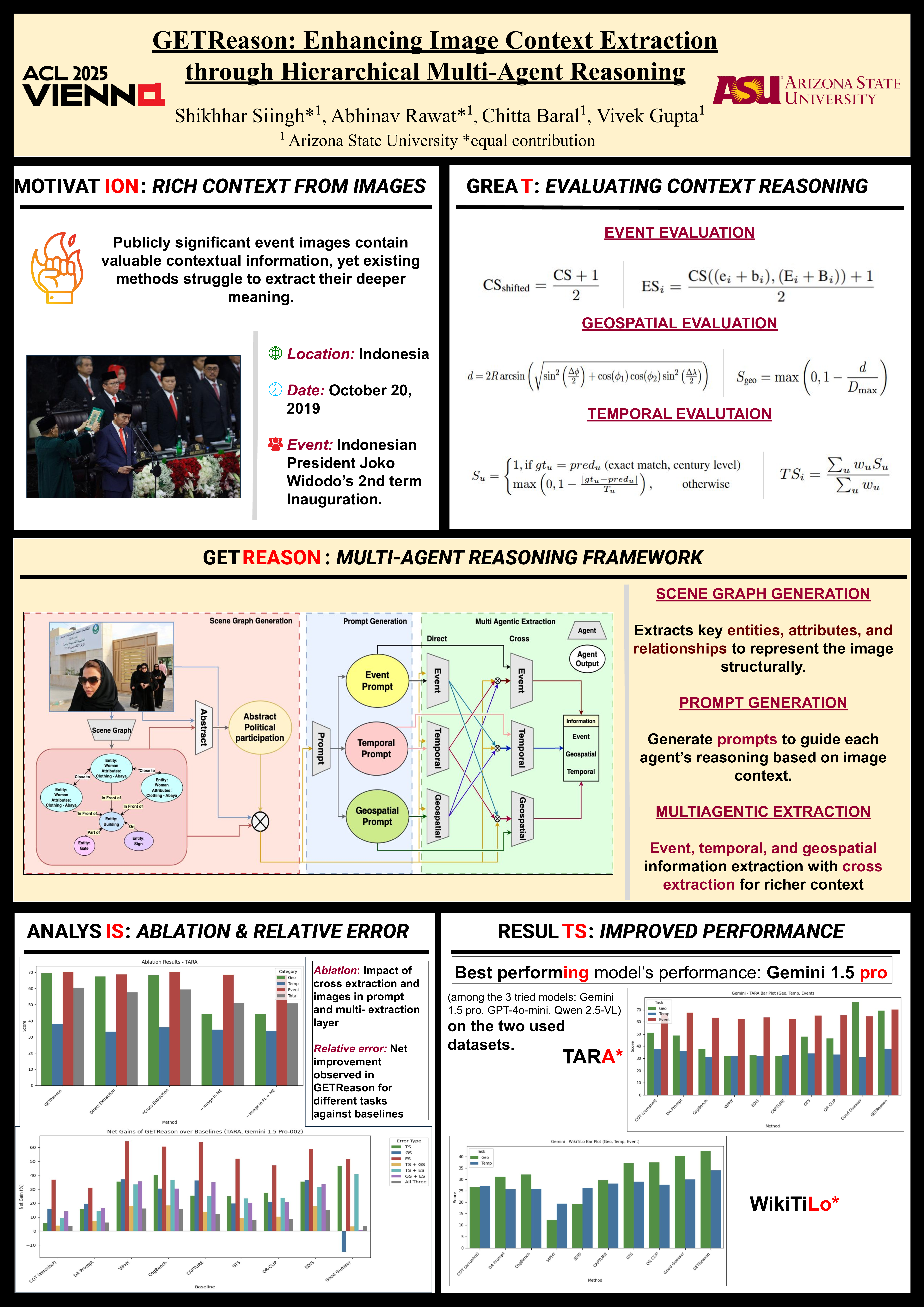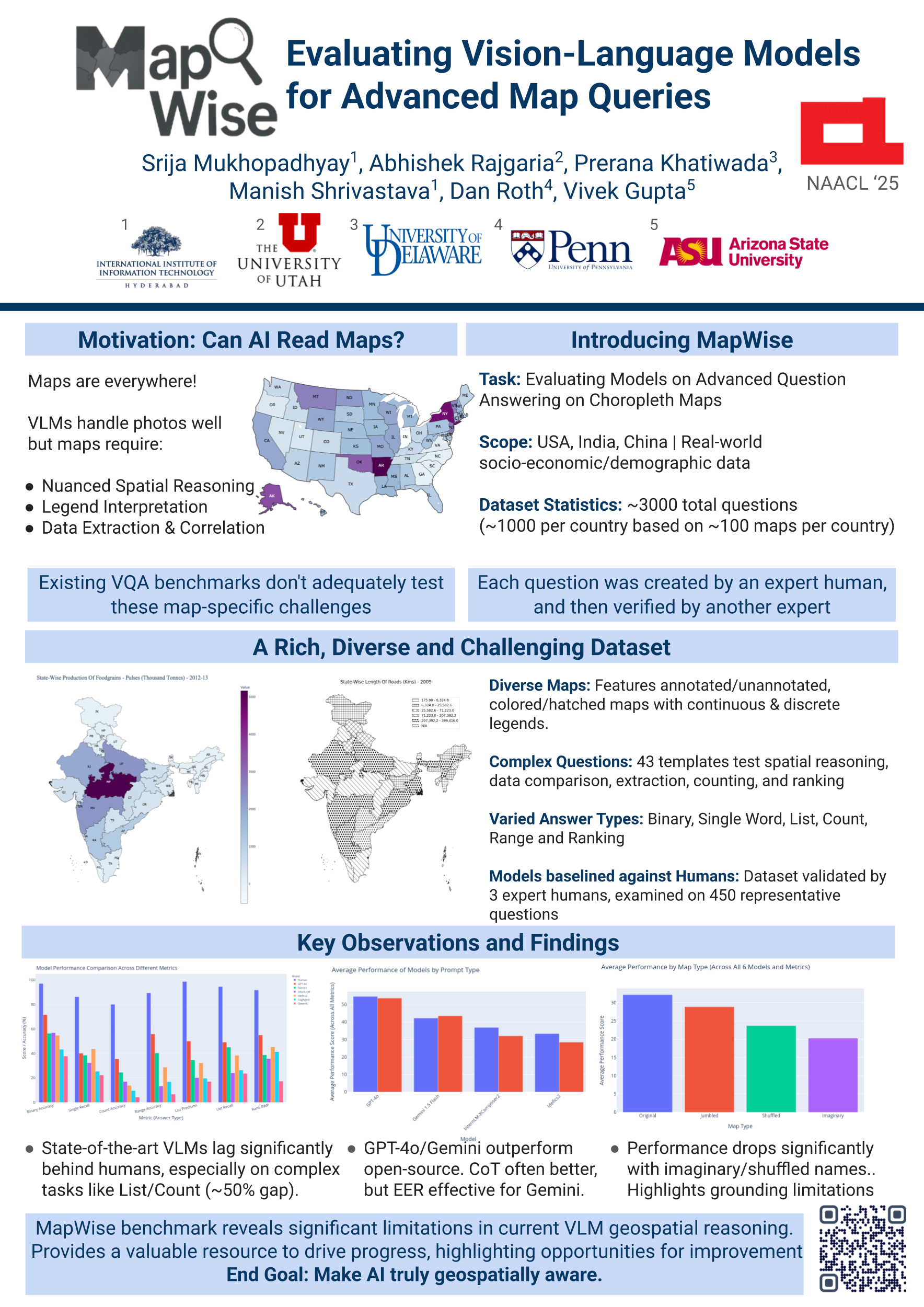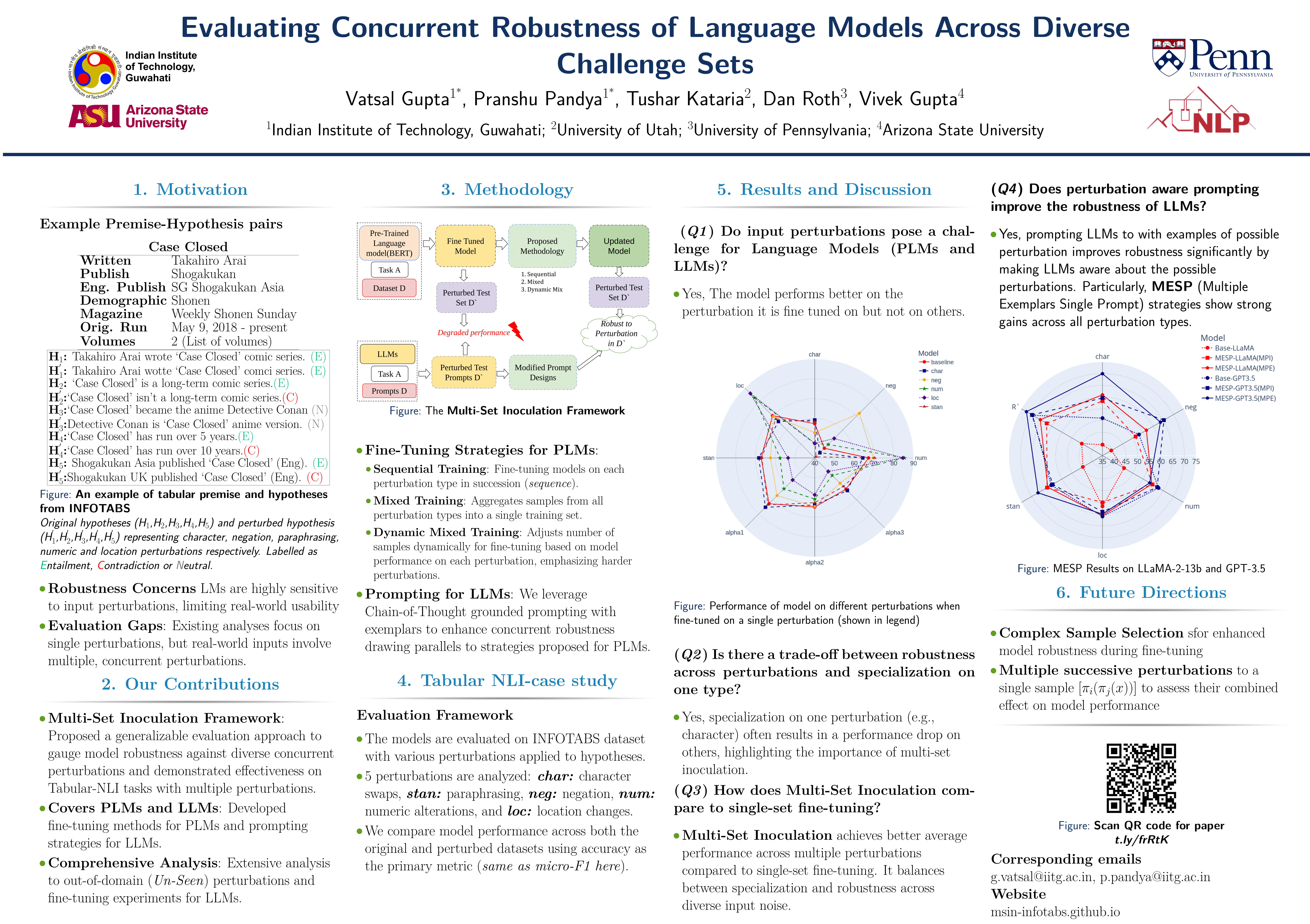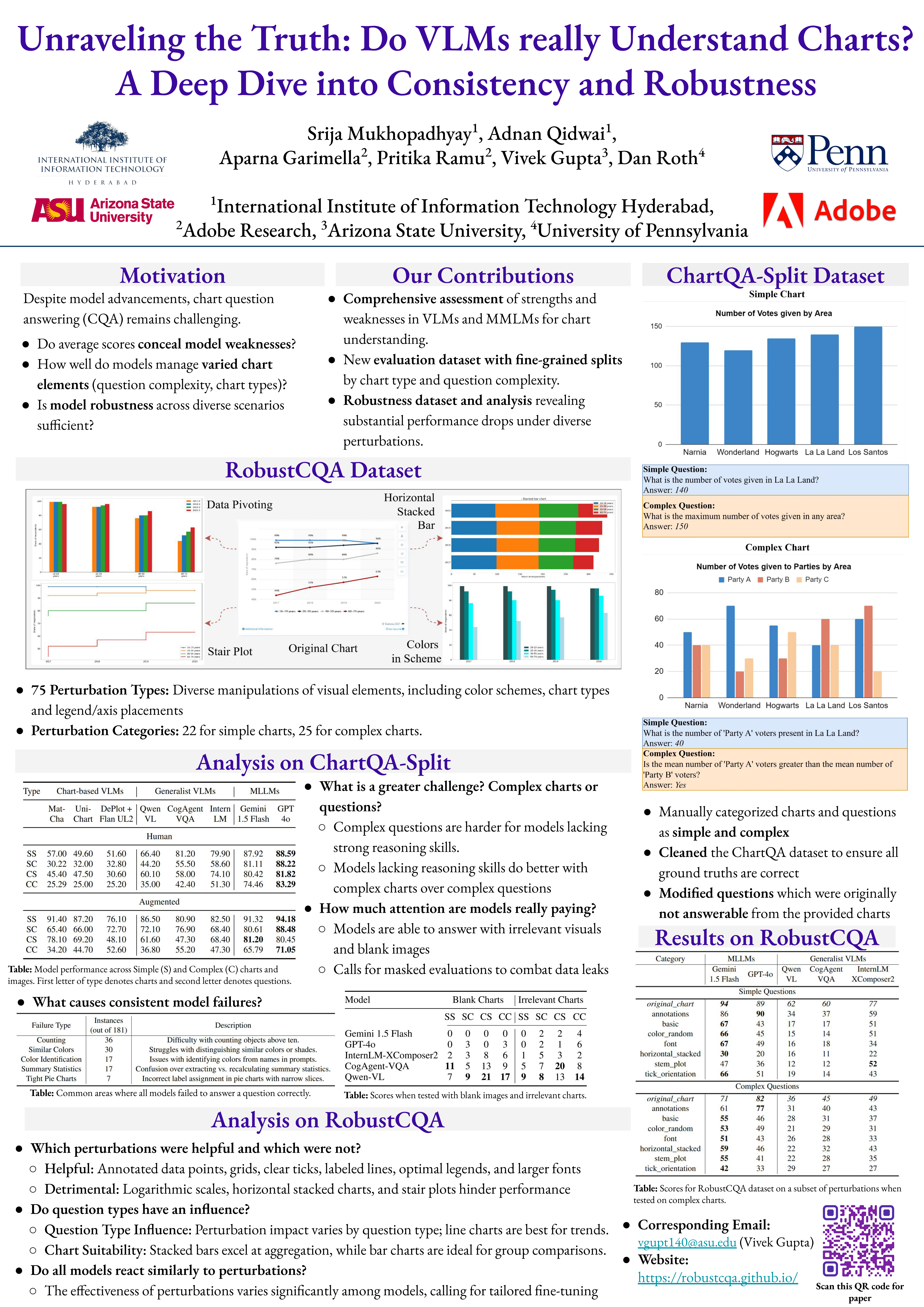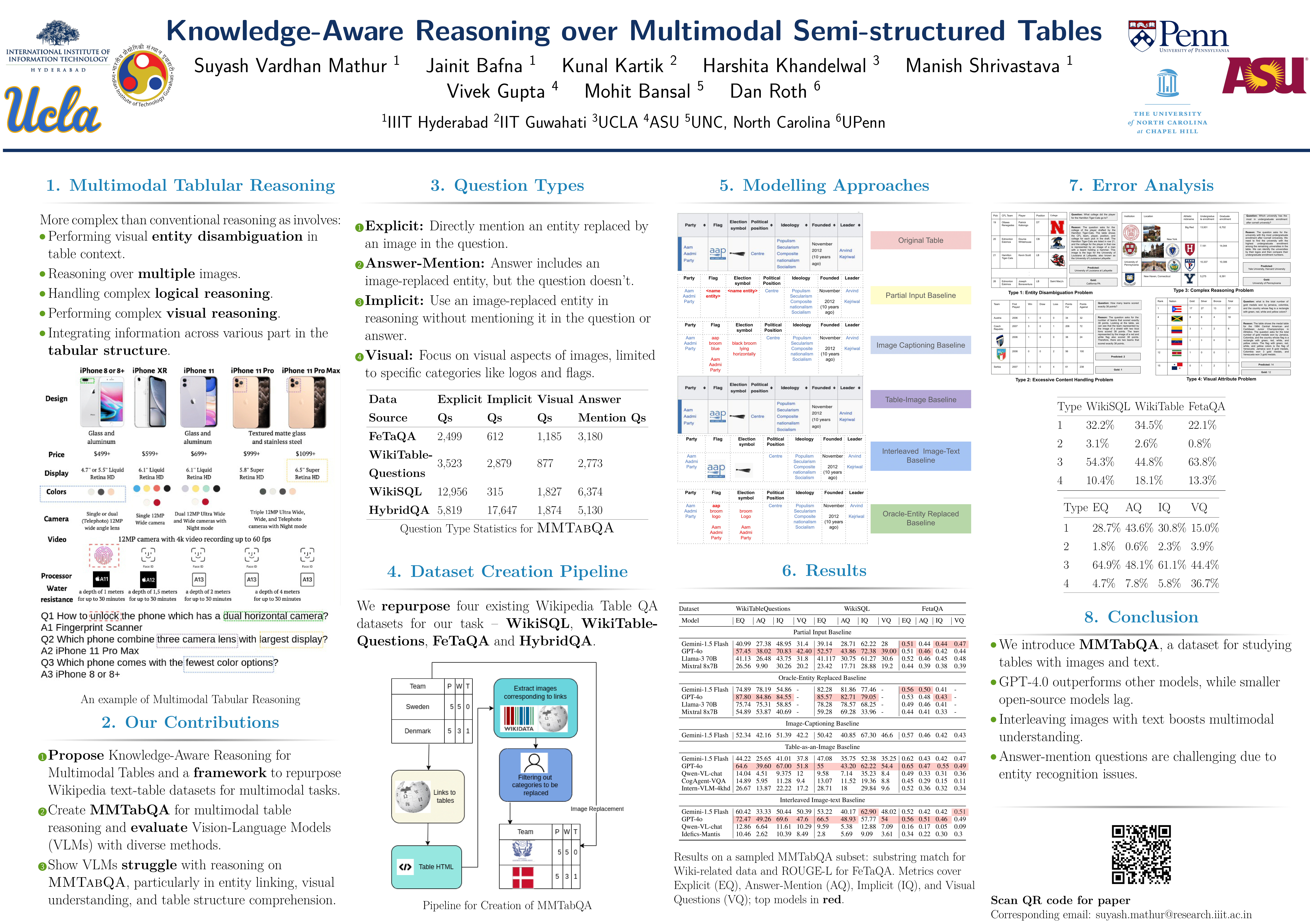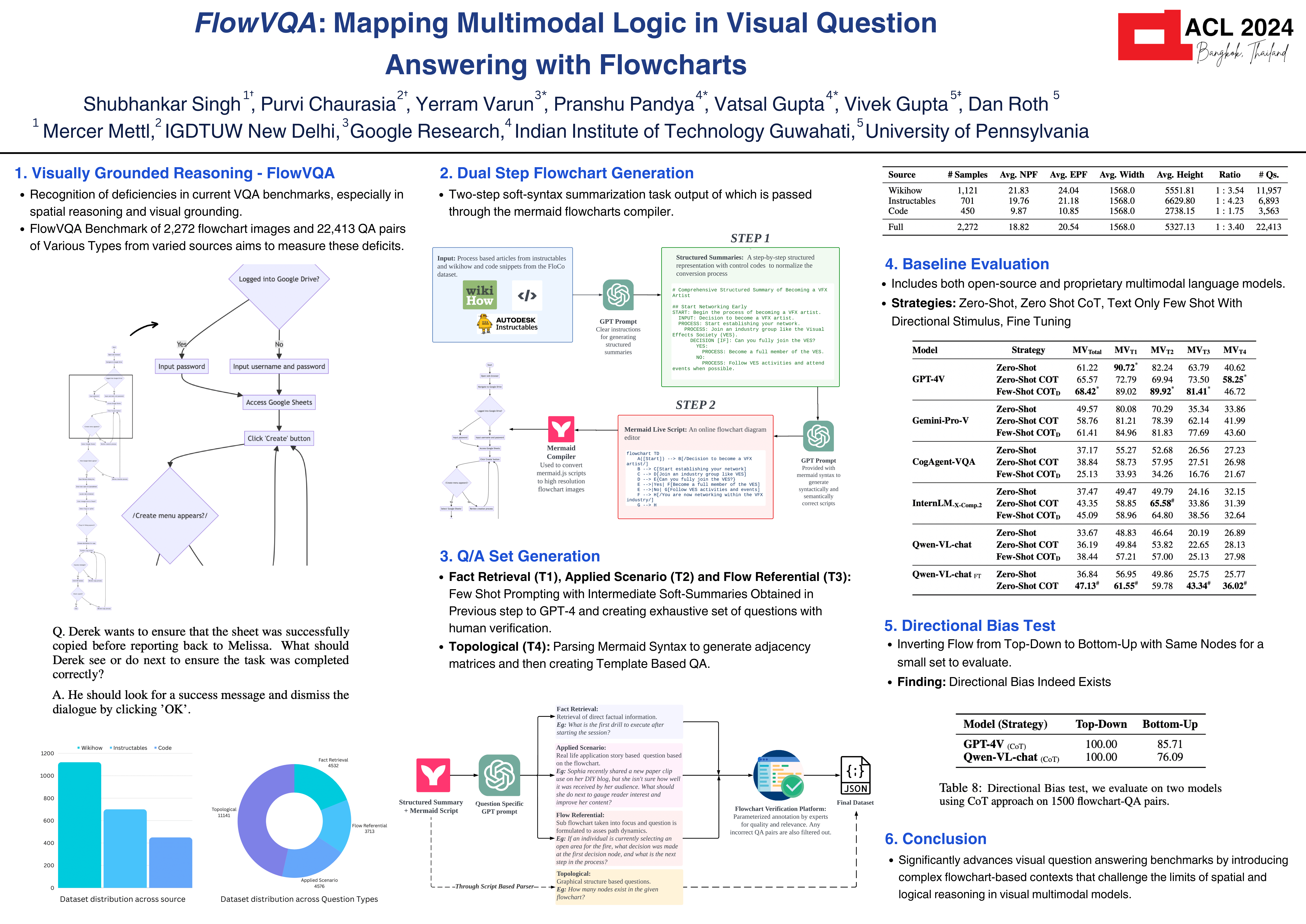
MAPVERSE: A Benchmark for Geospatial Question Answering on Diverse Real-World Maps
Maps are powerful carriers of structured and contextual knowledge, encompassing geography, demographics, in- frastructure, and environmental patterns. Reasoning over such knowledge requires models to integrate spatial re- lationships, visual cues, real-world context, and domain- specific expertise-capabilities that current large language models (LLMs) and vision–language models (VLMs) still struggle to exhibit consistently. Yet, datasets used to bench- mark VLMs on map-based reasoning remain narrow in scope, restricted to specific domains, and heavily reliant on artificially generated content (outputs from LLMs or pipeline-based methods), offering limited depth for evaluat- ing genuine geospatial reasoning. To address this gap, we present MAPVERSE, a large-scale benchmark built on real- world maps. It comprises...